The long-term care insurance program
Long-term care insurance is a public social insurance program run by municipal governments to provide long-term care services. Membership is mandatory for those 40 years of age or older. Under the long-term care insurance system, Health Insurance Societies collect long-term care insurance premiums on behalf of the long-term care insurance program from category 2 insured persons who are members of the Society.
- Who is eligible for long-term care insurance?
- Long-term care insurance premiums
- Details of long-term care insurance services
Who is eligible for long-term care insurance?
Insured persons aged 40 and older are eligible for long-term care insurance. These individuals are categorized as shown below by age, etc. In contrast to health insurance, this program lacks the category of “dependents”. All members are considered insured persons.
- *In some cases, persons aged 40 or above are exempt from long-term care insurance. See the Procedures page for more information.
| Persons aged 65 and above | Category 1 insured persons |
|---|---|
| Members of medical care insurance aged 40 through 64 (Insured persons, dependents) |
Category 2 insured persons |
The long-term care insurance system
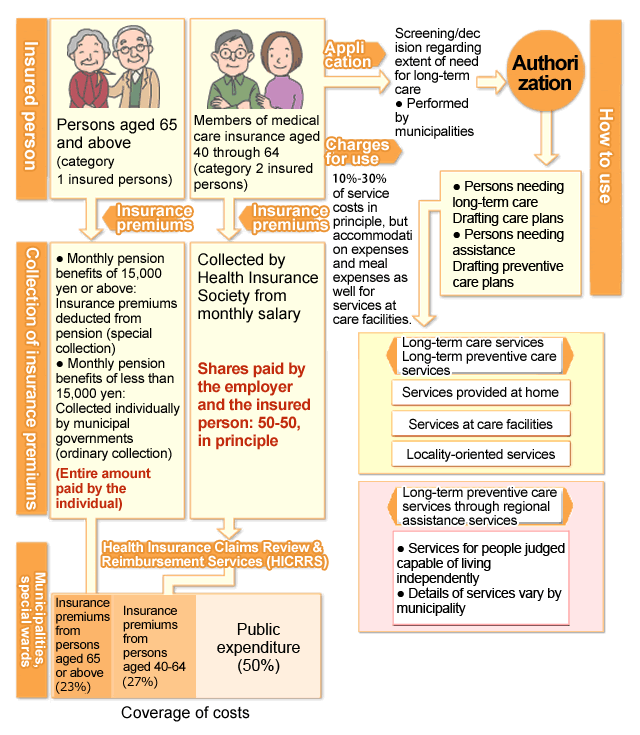
Copayments for long-term care services will be 10% (20% or 30% for high-income earners) of the cost of the services, depending on the user’s ability to pay. You can check your copayment on the Long-term Care Insurance Copayment Certificate issued to persons needing support or long-term care.
| Copayment | Income standard |
|---|---|
| 20% |
|
| 30% (from August 2018) |
|
- * Notwithstanding the above, copayments are 10% for Category 2 insured persons, those exempt from paying municipal tax, and those receiving public assistance.
- * If your copayment for long-term care exceeds 44,400 yen in a month (measures are available to reduce this amount for low-income earners and other eligible persons), then the amount in excess of this amount will be refunded as high long-term care service costs.
Long-term care insurance premiums
As outlined below, the amount of long-term care insurance premiums and how they are collected varies by category of insured person.
Long-term care insurance premiums for a category 1 insured person
| Collection method | Collected by municipalities. Collected directly from pension if pension benefits total 15,000 yen or more per month. Collected individually if pension benefits total less than 15,000 yen per month. |
|---|---|
| Calculation method | Insurance premiums are determined by multiplying the base amount established by the ordinance of each municipality by an income-dependent insurance premium rate. |
Long-term care insurance premiums for category 2 insured person
| Collection method |
|
|---|---|
| Calculation method | Value obtained by multiplying the standard monthly remuneration and the standard bonus by the long-term care insurance premium rate (varies by Health Insurance Society) |
- Insurance premiums are collected in proportion to compensation (standard remuneration). *1
- Long-term care insurance premiums for dependents aged 40 to 64 are included in the long-term care insurance premiums for insured persons aged 40 to 64; therefore, dependents do not need to pay their own long-term care insurance premiums.*2
- Regarding long-term care insurance premiums during childcare leave, employers can submit applications to exempt both themselves and the insured persons in the same way as for general insurance premiums.
- Individuals seconded overseas are exempt from long-term care insurance premiums.*2
- In principle, employers are responsible for half of insurance premiums.
- Voluntarily and continuously insured persons and special-case retired insured persons are responsible for paying the entirety of long-term care insurance premiums in the same way as for general insurance premiums.
- *1 The bylaws of health insurance societies approved by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare can set out fixed amounts for insurance premiums according to income tiers rather than fixed percentages of standard remuneration.
- *2 The bylaws of some health insurance societies and some mutual aid associations set out provisions for the collection of long-term care insurance premiums from insured persons aged 39 or younger with dependents aged 40 to 64, or insured persons living outside Japan (specific insured persons). This health insurance does not collect these premiums in these cases.
Method of determining long-term care insurance premiums for Category 2 insured persons
- Health Insurance Claims Review & Reimbursement Services (HICRRS) notifies medical care institutions of the amounts of long-term care insurance benefits calculated according to the number of Category 2 insured persons enrolled.
- Each insurer calculates long-term care insurance premium rates by dividing the total amount allocated to them by the total amount of standard remuneration of all Category 2 insured persons. Long-term care insurance premium rates are revised each fiscal year.
- Category 2 insured persons’ individual long-term care insurance premiums are their standard monthly remuneration multiplied by the long-term care insurance premium rate.
Details of long-term care insurance services
As shown below, long-term care insurance services include “services provided at home”, “services provided at care facilities”, and “locality-oriented services”.
Services provided at home
- Services provided on visits to the patient at home or elsewhere
Long-term care on a visitation basis, nursing on a visitation basis, bathing service on a visitation basis, rehabilitation on a visitation basis, instructions for medical care at home - Services provided at care facilities
Long-term care at care facilities, rehabilitation at care facilities, short-term stay for livelihood care, short-term stay for medical and long-term care, therapy for persons staying at specified facilities - Services providing a care environment
Lending of welfare appliances, aid for purchases of welfare appliances, allowances for modifying homes
Services provided at care facilities
These services are available only for those judged as needing long-term care.
- Welfare facilities for the elderly requiring long-term care (special nursing homes for the elderly)
- Health facilities for the elderly in need of long-term care (health services facility for the aged)
- Integrated facilities for medical and long-term care
- Note: As a general rule, new patients accepted for inpatient care at special nursing homes for the elderly will be restricted to those in the category of persons needing long-term care 3 and above.
Locality-oriented services
This is a framework for providing a wide range of flexible services to enable those who need long-term care to continue living in their familiar home communities.
These services are operated by individual municipal governments. In principle, they are available for use only by residents of the municipality.
- Small-scale multifunctional long-term care at home
- Group homes for elderly persons with acknowledge Syndrome
- Daytime services available for dementia patients
- Nighttime long-term care on visitation basis
- Daily Life Long-Term Care for a Person Admitted to a Community-Based Specified Facility
- Admission to a Community-Based Facility for Preventive Daily Long-Term Care of the Elderly Covered by Public Aid
- Nursing on a visitation basis of regular rounds and on-demand response(beginning April 2012)
- Nursing and small-scale multifunctional domiciliary care services (combination services)
For what types of long-term care services is a category 2 insured person eligible?
Category 2 insured persons aged 40-64 are eligible to receive long-term care services under long-term care insurance only if they suffer from one of the following specified diseases and disorders. Category 1 insured persons aged 65 or above are eligible to receive the services whatever the condition or disorder.
- Pre-acknowledge syndrome
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig's Disease)
- Parkinson's disease-related conditions
- Spinocerebellar degeneration
- Multiple system atrophy
- Diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy
- Arteriosclerosis obliterans
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Degenerative joint disease with pronounced deformation of both knee or hip joints
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament
- Stenochoria of the spinal canal
- Osteoporosis involving bone fractures
- Progeria
- Terminal cancer